Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) – Natural Therapies
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid Arthritis is a serious autoimmune disease, characterised by chronic inflammation and thickening of the synovial lining (membranes around the joints) eventually leading to cartilage destruction. In autoimmune diseases the immune system attacks body cells and tissues as if they were foreign invaders.
Contributing factors are thought to include food allergies, leaky gut syndrome, microbes, and hereditary influences.
RA affects approximately 3% of the population, is three times as common in women as it is in men, and typically starts between the ages of 20-40. There is a form of arthritis that affects much younger people – some from infancy, up to the age of 16. This is called Juvenile Idiopathic (meaning no known cause) Arthritis or Arthropathy (JIA).
Signs and Symptoms
- Chronic fatigue and weakness
- Low grade fever
- Joint stiffness and pain
- Painful, swollen joints
- Weight loss
- Painful and deformed joints
Possible Causes:
- Genetic susceptibility.
- Leaky gut syndrome: The healthy bowel provides us with a complex and effective barrier against the thousands of toxins, organisms, and foreign molecules that we ingest daily. When this barrier mechanism breaks down undesirable substances penetrate the ‘leaky bowel’ and are exposed to the body’s immune system and in some cases stimulate the body to attack immunologically similar tissues (such as joints).
- Poor diet
- Dysbiosis: Refers to an imbalance and reduction of the good microbes within the bowel wall. These normally help to protect the integrity of the bowel wall, as well as helping to produce key nutrients.
Complementary Strategies
The following information does not constitute a prescription or recommendation – this is included for your information only.
Biochemical strategies
Dietary Modifications
Increase complex carbohydrates, dietary fibre, fruits, vegetables, and nuts. Increase foods containing omega-3 fatty acids – it is best to utilise plant sources of these to avoid issues with heavy metal and other chemical toxicity – search for ‘vegan Omega 3s’.
Some people are sensitive to various foods to experiement with reducing or avoiding refined and processed foods, eliminate dairy products, check sensitivities to citrus foods and finally, the ‘nightshade foods’ can worsen symptoms in some people – these include: tomatoes, white potatoes, egg plant, peppers.
Sulphur containing foods are found to be beneficial; these include cabbage, Brussels sprouts, garlic, and onions.
Supplements:
Glucosamine Sulphate: Can help to repair the damaged connective tissue.
Vitamin B6: Has been shown to reduce the inflammatory cytokines involved in rheumatoid arthritis.
Boron: The Rheumatoid Disease Foundation suggests the use of boron to treat Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoporosis. Boron is said to play a role in the retention of calcium, as well as stimulating hormonal factors that contribute to healthy bones. Boron-rich foods include alfalfa, peas, cabbage, apples, and prunes.
Essential Fatty Acids
These work by inhibiting the prostaglandins that cause pain and inflammation. The most potent fatty acid is GLA (gamma linoleic acid) available in evening primrose oil, borage oil, and black currant seed oil.
Sea cucumber has been used for thousands of years to relieve arthritis. It is a rich source of specific lubricating compounds found abundantly in all connective tissue, especially the joints and joint fluid. It may take 3 to 6 weeks to notice an improvement.
Bromelain is an enzyme from the pineapple plant, and is especially effective in reducing the inflammation from arthritis. Eat fresh pineapple frequently.
Herbal Therapy
Ginger can give you significant pain and inflammation relief. Take 100 mg daily in supplement form, or include fresh ginger in your diet.
Boswelia is anti-inflammatory in action, and is very effective in treating arthritis and other inflammatory conditions. Take 400 mg to 800 mg daily in divided doses, with meals.
Feverfew inhibits the production of prostaglandins and thereby relieves pain and inflammation. It also reduces the production of the inflammatory components of white blood cells. Take 100 mg daily with meals.
- Persistent stress, triggering hormonal imbalances
- Infectious agents
Tests and Investigations
Medical History
This is how the patient describes the symptoms and when and how they began. Good communication between the patient and doctor is especially important.
Physical examination
This will include an examination of the joints, skin, reflexes, and muscle strength.
Laboratory Tests
Include testing for rheumatoid factor, an antibody that is present in most people with rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Other tests would look for the presence of inflammation in the body (CRP or ESR test), a white blood cell count, and a haemoglobin test for anaemia.
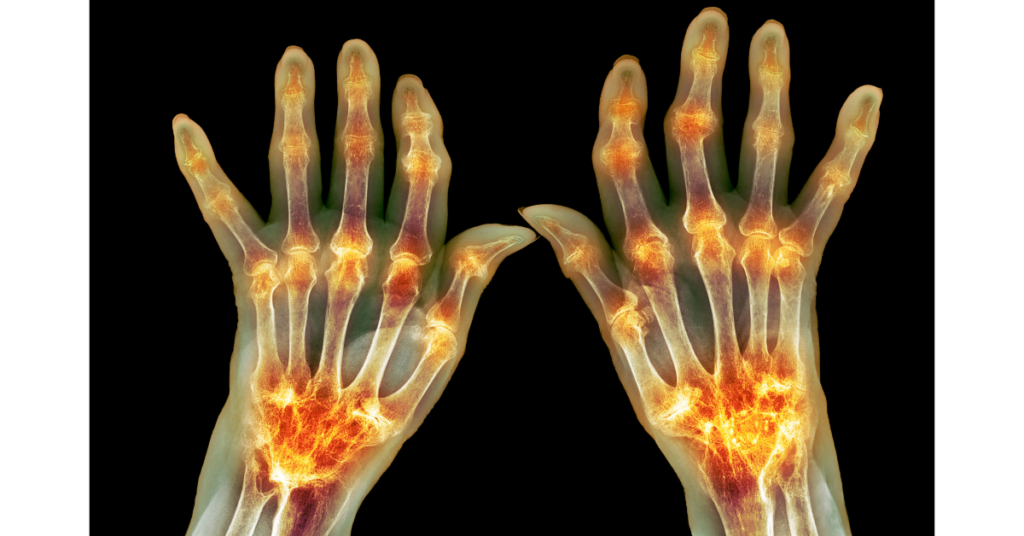
X-rays
Used to determine the degree of joint destruction and to monitor progress of the disease.
Conventional Treatment Strategies
| Medications | Uses | Side effects |
| Aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatories Examples include: Ibuprofen and Voltarol. | To reduce pain, swelling and inflammation, allowing patients to move more easily and carry out normal activities. Generally part of early and continuing therapy. | Upset stomach. Tendency to bruise easily. Fluid retention (NSAIDs other than aspirin). Ulcers |
Possible kidney and liver damage (rare). Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) Examples: Gold, penicillamine, antimalarials, sulfasalazine. Used to alter the course of the disease and prevent joint and cartilage destruction. May produce significant improvement for many patients.
Exactly how they work is still unknown.
Generally take a few weeks or months to have an effect..
Patients may use several over the course of the disease. Toxicity is an issue*. DMARDs can have serious side effects: Gold: Skin rash, mouth sores, upset stomach, kidney problems, low blood count. Antimalarials: Upset stomach, eye problems (rare).
Penicillamine: Skin rashes, upset stomach, blood abnormalities, kidney problems.
Sulfasalazine: Upset stomach. Immuno-suppressants (also considered DMARDs) Examples :
- Methotrexate
- Azathioprine
- Cyclophosphamide
Used to restrain the overly active immune system, which is key to the disease process. Same concerns as with other DMARDs: Potential toxicity and diminishing effectiveness over time.
Methotrexate: Also used as a chemotherapy drug for some cancers can result in rapid improvement; appears to be very effective.
Azathioprine: First used in higher doses in cancer chemo-therapy and organ transplantation; used in patients who have not responded to other drugs; used in combination therapy.
Cyclo-phosphamide: Also used in higher doses in cancer chemotherapy; effective, but used only in very severe cases of rheumatoid arthritis because of potential toxicity.
Toxicity is an issue*. Immunosuppressants can have serious side effects: Methotrexate: Upset stomach, potential liver problems, low white blood cell count.
Azathioprine: Potential blood abnormalities, low white blood cell count, possible increased cancer risk.
Cyclophosphamide: Low white blood cell count, other blood abnormalities, increased cancer risk.
Corticosteroids (also known as glucocorticoids) Examples:
- Prednisone
- Deltasone, Orasone
- Methylprednisolone (Medrol)
Used for their anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. Given either in pill form or as an injection into a joint.
Dramatic improvements in very short time
Potential for serious side effects, especially at high doses
Often used early while waiting for DMARDs to work
Also used for severe flares, and when the disease does not respond to NSAIDs and DMARDs
Osteoporosis
Mood changes
Fragile skin, easy bruising
Fluid retention
Weight gain
Muscle weakness
Onset or worsening of diabetes
Cataracts
Increased risk of infection
Hypertension (high blood pressure)
Biological therapies
These are a much newer class of drugs that directly affect the production on pro-inflammatory cytokines – they have the potential to produce serious side effects, but for many users they can be life changing.
Surgery
Several types of surgery are available to patients with severe joint damage. These procedures can help reduce pain, improve the affected joint’s function and appearance, and improve the patient’s ability to perform daily activities.
Structural Strategies
Exercise
Always consult with your doctor prior to commencing any exercise program.
Keep moving. Exercise is an excellent way to prevent and treat arthritis. The keys are to not over stress your joints, and to work within your limits of tolerance. Exercise’s many other benefits to mind and body include:
- Reducing stress
- Enhancing sleep
- Improving your physical capabilities
- Promoting relaxation
- Increasing your resistance to disease
- Improving sexual function, satisfaction
- Preventing joint deformities
- Helps to achieve optimal weight
Always discuss with your doctor about trying and combining a combination of stretching exercises, mild strengthening exercises (such as lifting weights) and low-impact aerobic exercises (such as swimming, walking, or bicycling).
Alexander Technique
The Alexander Technique is a process of re-education, which aims to rediscover our natural poise and freedom, and to use our bodies more efficiently. It can lead to a release of unnecessarily contracted muscles, a freeing up of joints and a lengthening of the spinal column.
Energy Strategies
Magnet Therapy
Magnet therapy represents one of the cheapest and most widely available forms of energy therapies available. Used by healers for more than 3,000 years and thousands of arthritis sufferers worldwide – works for some, but does not provide a good level of pain relief for all people.
How it works is controversial, my theory, however, is that applying static magnets activates the body’s natural healing mechanisms by helping cells to regain their natural electromagnetic field.
Microcurrent Therapy
A new generation of TENS machine has emerged called ACE. This innovative pain relief system delivers a phased programme of microcurrents designed to mimic the body’s natural electrical currents and in doing so stimulate tissue repair and regeneration. The claimed benefits are:
- Instant pain relief
- Increased joint and muscle mobility
- Injury heals faster and stronger
- Reduction in swelling
- Good night’s sleep
Acupuncture
Has been clinically proven to help with the symptoms and pain control of people with arthritis.
Psycho-Social Strategies
Meditation
Focusing on a particular object produces a state of ‘relaxed awareness’ that reduces stress and perception of pain. (See also Visualisation)
Relaxation
Spend more time on activities that relax you. For example, listening to music can have a temporarily beneficial affect on blood pressure levels.