Psoriasis – Natural Health Approaches that Really Work
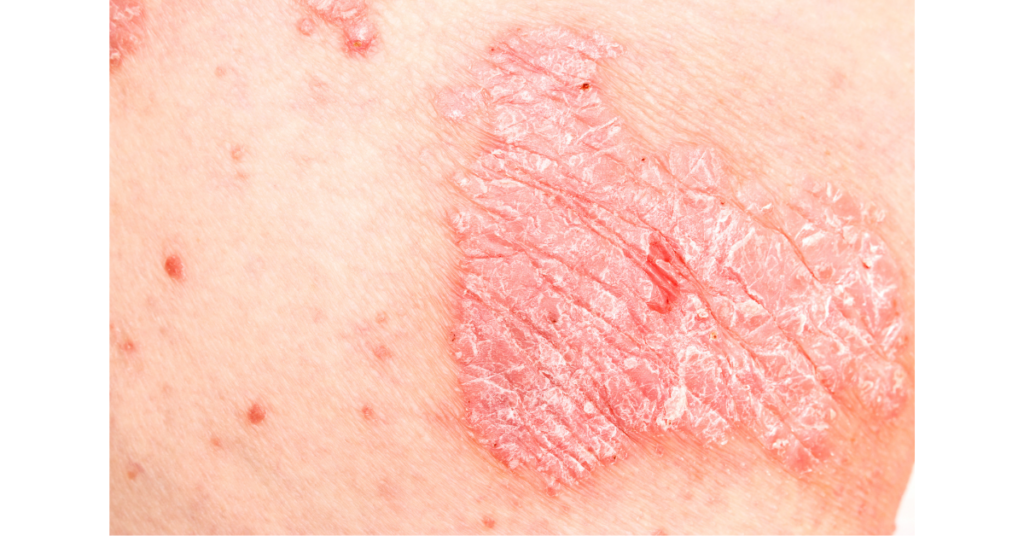
Psoriasis is a commonly occurring condition that happens as a result of the top layer of the skin – the epidermis – overproducing skin cells. The cells are immature and are not able to be integrated into normal healthy skin.
The result is raised, reddened skin patches that are covered with silvery grey scales. These can be very itchy, and many sufferers feel disfigured by the disease.
The cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is usually hereditary, and autoimmunity and potentially a metabolic disorder is thought to be at the root of the problem.
Many sufferers also notice that the condition becomes worse when they are stressed.
Conventional medical treatments may include the use of coal tar soaps and shampoos, and ultraviolet light treatment.
These treatments are not curative and, as soon as these treatments are stopped, symptoms return.
Complementary Treatments
The following information does not constitute a prescription or recommendation – this is included for your information only.
As with all forms of complementary medicine, it is the person who is treated, not the disease.
This means that while several people may come to a complementary medical practitioner with a skin complaint diagnosed conventionally as psoriasis, the actual treatment given to each of these individuals may vary.
Naturopathy
Many naturopaths believe that psoriasis occurs as a result of an overgrowth of bacteria in the bowel. Because of this, colon cleansing programmes and probiotics – the beneficial gut bacteria – may be prescribed, along with a general detoxification and hydrotherapy programme.
Plant-Based Approaches to Managing Psoriasis
Turning to nature, several plant-based remedies show promise in soothing psoriatic symptoms:
- Aloe Vera: Renowned for its skin-healing properties, aloe vera can reduce redness and scaling associated with psoriasis.
- Turmeric (Curcumin): With its potent anti-inflammatory properties, turmeric can help reduce psoriasis flare-ups.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in flaxseeds and walnuts, omega-3s are known for their anti-inflammatory effects and can be beneficial for psoriatic skin. It is best to utilise plant sources of these to avoid issues with heavy metal and other chemical toxicity – search for ‘vegan Omega 3s’.
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antibacterial properties, tea tree oil can help prevent infection in psoriatic skin lesions.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to plant-based remedies, lifestyle changes can have a significant impact:
- Stress Reduction: Yoga, qigong, and meditation can be effective in managing stress, a known trigger for psoriasis.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts can support skin health.
- Sun Exposure: Moderate sun exposure can improve symptoms, but it’s important to avoid sunburn.
Homoeopathy
Homoeopaths will look for the underlying cause of psoriasis and treat that as opposed to treating the psoriasis itself. Psoriasis is viewed by homoeopaths as evidence of a strong “psoric miasm”. A miasm is an inherited predisposition to certain groups of diseases – which would include psoriasis. This is in line with conventional thought that acknowledges the genetic link as a causative factor. Homoeopaths also agree that mental and emotional factors such as stress contribute to exacerbation of the problem.
Any one of the two thousand plus homoeopathic remedies may be prescribed for a person with psoriasis since homoeopathy is such an individualised form of treatment and there are no standard psoriasis remedies. Sulphur, however, is one remedy which might tend to fit in well with the general “Psoric” patients constitutional picture – but with all chronic conditions it is imperative that a professional homeopath is consulted.
Ayurveda
Practitioners believe that psoriasis is caused predominantly by blood impurities and strong emotional factors. The recommended treatments will usually be with herbal remedies that will cleanse the blood and stimulate the liver. Massage therapies, meditation and yoga exercises may also be prescribed.
Psoratherpie
This therapy is where conventional and complementary medicine meet.
In the Eastern European countries – particularly Bulgaria and Russia, there is a distinct science called “psoratherapie”.
It is a specific treatment for psoriasis, however, it employs a combination of different complementary medical approaches – although as in conventional medicine, the treatment for each patient, regardless of their precise individual symptoms is the same.
Treatment consists of application of a special type of mud that smells very strong due to its high sulphur content. This is quite interesting because homoeopathic medicine often uses sulphur to treat psoriasis.
In addition, phytotherapy – treatment with herbs – will be recommended, which may be taken as a tea or in a bath. These herbs will be prescribed to suit the individual and will differ from person to person.
The patient will receive light treatment in a “psorarium”; a chamber built especially for the purpose of treating psoriasis and lastly, salt-water baths may be prescribed.
Hypnotherapy
Hypnotherapy and visualisation have been shown to greatly reduce stress levels. Given that psoriasis seems to have a very strong stress related component, it is not surprising therefore that these measures are effective.
With advances in the new science of psychoneuroimmunology (PNI) there is a great deal of research into the link between the mind and body. PNI theories postulate that the mind can affect the immune system and it has certainly been proven that visualisation of pleasurable situations actually does boost the immune system.
Furthermore, there is a great deal of evidence to suggest that patients who undergo guided visualisation exercises can affect changes in their physiology, and much groundbreaking and highly successful work has been done with patients who experience skin disorders.
Further Reading and Resources
To deepen your understanding, we recommend exploring the following resources:
- “Healing Psoriasis: The Natural Alternative” by Dr John O.A. Pagano.
- The National Psoriasis Foundation website for comprehensive information on psoriasis management.
- “Anti-Inflammatory Diet for Psoriasis” by Paul S. Yamauchi, which explores dietary approaches to managing psoriasis.
The management of psoriasis through lifestyle changes, particularly focusing on dietary interventions, has been a topic of considerable research interest. Here’s a summary of the key findings from recent studies:
1. Dietary Interventions and Exercise: Research published on PubMed highlights that dietary interventions can potentially reduce the severity of psoriasis, especially in obese individuals. These interventions, when combined with exercise programs, may further improve psoriasis severity and Body Mass Index (BMI).
- Study: “Lifestyle changes for treating psoriasis”
- Source: PubMed
- Details: This study suggests that dietary intervention may reduce the severity of psoriasis and probably improves quality of life and reduces BMI in obese people when compared with usual care. Additionally, a combined dietary intervention and exercise program probably improves psoriasis severity and BMI when compared with information only.
2. The Role of Diet in Psoriasis Management: A comprehensive review in the Nutrition Research Reviews emphasizes the growing evidence supporting the role of diet in managing psoriasis. The review indicates that people living with psoriasis often have different dietary intakes compared to controls, with higher fat and lower fiber intakes noted. Lower psoriasis severity has been associated with higher fiber intake. However, it’s important to note that while certain dietary approaches have shown improvements in psoriasis symptoms, these findings are primarily applicable to specific populations, such as individuals with obesity and coeliac disease.
- Study: “The role of diet in the management of psoriasis: a scoping review”
- Source: Nutrition Research Reviews
- Details: This review indicates that people living with psoriasis often have different dietary intakes compared to controls, with higher fat and lower fiber intakes noted. Lower psoriasis severity has been associated with higher fiber intake. However, specific dietary approaches improved symptoms, but only in specific populations.
3. Weight Loss and Disease Severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis in the International Journal of Obesity suggests that weight loss interventions can significantly impact the severity of psoriasis in obese patients. This finding is particularly relevant as it underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy weight as part of psoriasis management.
- Study: “Effect of lifestyle weight loss intervention on disease severity in patients with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis”
- Source:
- van Acht MR, van den Reek JMPA, de Jong EMGJ, Seyger MMB. The Effect of Lifestyle Changes on Disease Severity and Quality of Life in Patients with Plaque Psoriasis: A Narrative Review. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2022 Apr 9;12:35-51. doi: 10.2147/PTT.S294189. PMID: 35433402; PMCID: PMC9007593.
- Details: This narrative review and meta-analysis suggest that weight loss interventions can significantly impact the severity of psoriasis in obese patients. It highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy weight as part of psoriasis management. The researchers also discuss the importance of relaxation interventions.
While more research is needed to establish specific dietary guidelines for psoriasis, current evidence suggests that dietary modifications, particularly those leading to weight loss in obese individuals, can have a positive impact on the management of psoriasis. It’s always advisable for patients to discuss any dietary changes with healthcare professionals to ensure these are suitable for their individual health needs and circumstances.